Overview of Condenser Microscopes
The condenser microscope is a vital tool in many scientific fields. It magnifies tiny details that the human eye can’t see. Central to this ability is the condenser. This component focuses light onto the sample. It improves clarity and contrast in the viewed image.
The role of the condenser in microscopy
The condenser plays a key role in microscopy. It collects and concentrates light, directing it onto the slide. This light then passes through the sample. Properly adjusted, the condenser ensures an even spread of light. This allows for sharp images with good resolution. A well-aligned condenser is crucial for high-quality observations.
Types of condensers and their applications
There are several types of condensers, each with unique benefits. Abbe condensers are common in basic lab microscopes. They work well for standard light microscopy. Achromatic condensers correct for color and focus on light better. They suit more demanding applications. Oil immersion condensers enable very high magnification. They’re best for viewing bacteria and other tiny organisms. Choosing the right condenser depends on the desired magnification level and the nature of the samples.
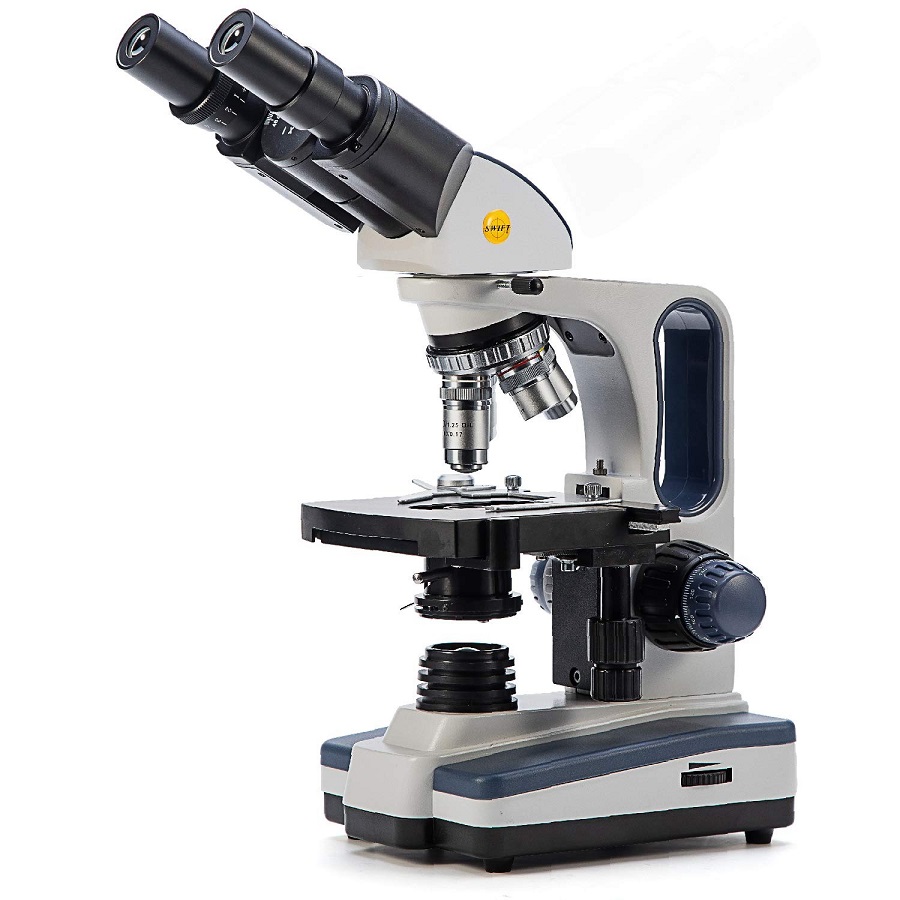
Key Features of a Condenser Microscope
A condenser microscope boasts several key features that are essential for precise imaging. Understanding these will help you utilize your microscope more effectively.
Aperture and resolution
The aperture of a condenser plays a crucial role in resolution. It controls the amount of light that reaches the sample. A larger aperture allows more light to pass through. This results in clearer, more detailed images. High resolution is vital for viewing minute structures. It defines the microscope’s ability to distinguish between two points that are close together. A high-quality condenser microscope should provide a balance between aperture size and resolution for optimal image clarity.
Working distance and light control
Working distance refers to the space between the condenser and the slide. It affects how easy it is to manipulate the sample under scrutiny. More working distance is helpful for larger samples or when adding chemicals. Light control is another important feature. It allows the user to adjust the brightness and contrast of the image. A microscope with good light control enables the user to observe samples under various lighting conditions. Both working distance and light control contribute to the versatility of the condenser microscope in a range of applications.
Selecting the Right Condenser for Your Needs
Choosing the right condenser for your microscope can be daunting. But with some know-how, you can make an informed choice. Identifying your needs is the first step. This will guide you towards the condenser that fits your application.
Criteria for choosing a condenser
When you select a condenser, keep in mind several factors:
- Magnification Needs: Match your condenser’s capabilities with the magnifications you use most.
- Sample Type: Consider the transparency and size of the specimens you’ll observe.
- Illumination Techniques: Your methods, like phase contrast or dark field, affect your choice.
- Budget Limits: Find a balance between cost and the features you require.
These criteria will help narrow down your choices. They ensure you don’t invest in a condenser that won’t suit your work.
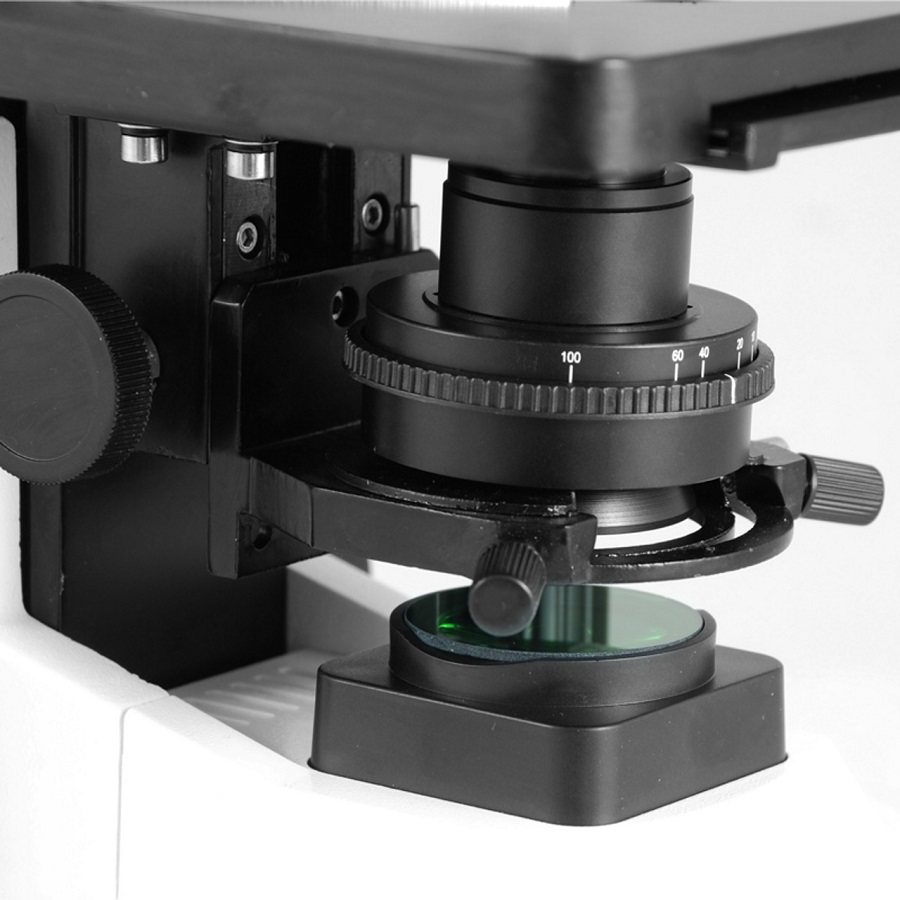

Comparison of the most popular condenser models
Let’s compare some widely used condenser models:
- Abbe Condensers: Standard in many labs, ideal for routine tasks.
- Achromatic Condensers: These correct for color and focus, fitting for detailed studies.
- Oil Immersion Condensers: For very high magnification, best for tiny organisms.
Each model offers its own strengths. Users must weigh these against their specific microscopy needs. A side-to-side comparison will make this easier. The right condenser microscope can transform your viewing experience, raising the quality of your work.
Innovative Uses of Condenser Microscopes
Condenser microscopes are not just for basic research. They are key in complex, cutting-edge studies. Their precision and flexibility open up new avenues in various fields.
Advanced techniques in biological research
Biologists value condenser microscopes for their ability to reveal micro-scale details. They utilize these tools in genetics, microbiology, and pathology. In genetics, condenser microscopes help visualize DNA strands. They show gene expression patterns in different cells. Microbiologists rely on them to study bacteria and viruses with high magnification. This makes it easier to understand their structures. Pathologists use condenser microscopes to examine tissues. These microscopes help identify illness markers not visible to the naked eye.
Industrial applications
Beyond biology, condenser microscopes contribute to industry. They are central in quality control. Manufacturers use them to inspect small parts, ensuring product standards. In electronics, they are essential for examining circuit boards. These tools detect flaws that could cause failures. Material scientists use them to analyze features of materials at the micro-level. Their findings often lead to the development of new, stronger materials.
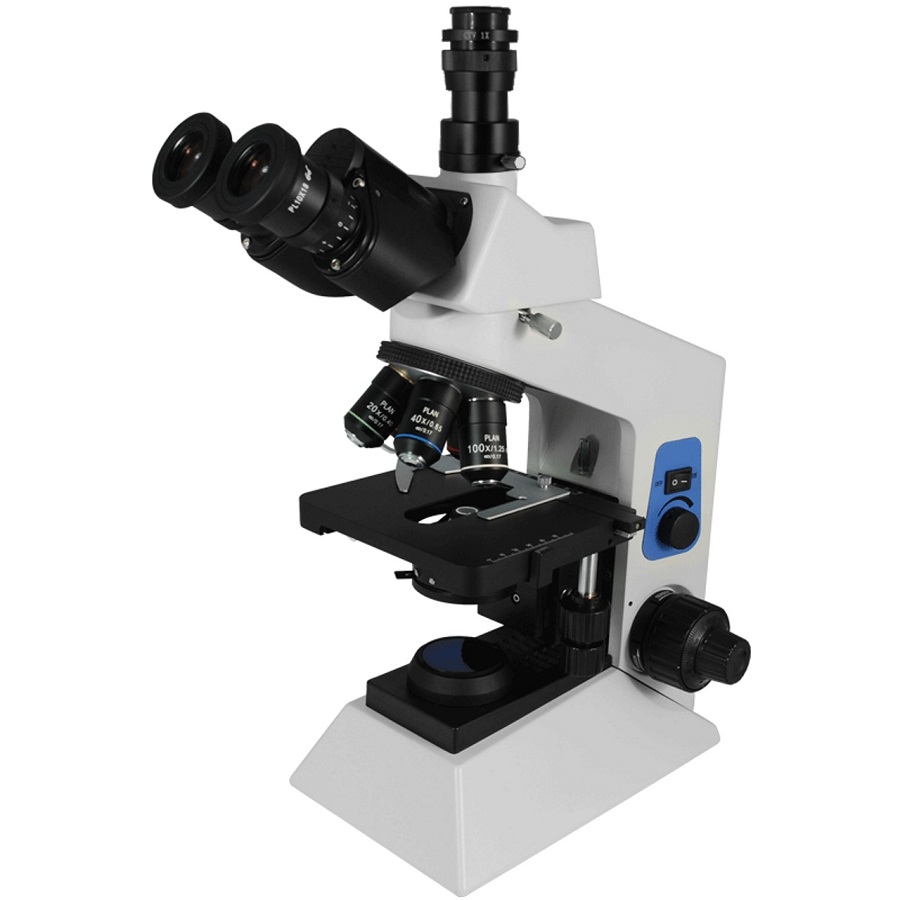
Maintenance and Care for Condenser Microscopes
Proper maintenance is essential for keeping your condenser microscope in top condition. Regular care increases longevity and ensures reliable results.
Cleaning and handling best practices
When it comes to cleaning and handling your condenser microscope, always:
- Turn off and unplug the microscope before cleaning.
- Use lens paper or a soft cloth to gently wipe the lenses.
- Avoid harsh chemicals that can damage lens coatings.
- Handle with care, especially when adjusting the condenser or objectives.
- Cover the microscope when not in use to protect it from dust.
Consistent maintenance prevents buildup that can obscure images and damage components.
Troubleshooting common issues
Even with care, you may encounter issues. Here are solutions for common problems:
- Blurry images: Check if the lenses need cleaning or if the condenser needs realignment.
- Difficult focus: Ensure the sample is properly mounted and the slide is clean.
- Lighting problems: Adjust the light source or replace the bulb if necessary.
- Mechanical resistance: If knobs are tight, consult the manual. Do not force them.
By addressing these issues promptly, you can preserve the quality and functionality of your condenser microscope.
Enhancing Microscopy with Condenser Accessories
To get the most out of a condenser microscope, pair it with the right accessories. These enhancements boost performance and add to your microscope’s versatility.
Objectives and eyepieces
Choosing the right objectives and eyepieces is crucial. They magnify the sample and work with the condenser to deliver sharp images. Wider eyepieces offer a greater field of view. High-power objectives let you see fine details. Match these parts to your microscope’s condenser to optimize viewing. Changing objectives and eyepieces can suit different magnifications or samples. This adaptability is key for varied research tasks.
Additional equipment for specialized tasks
For specific jobs, consider extra gear. Filter sets refine light for enhanced contrast and detail. Digital cameras capture images for analysis or record keeping. Sliders enable advanced techniques like phase contrast or dark field microscopy. These accessories work with the condenser microscope to tackle specialized tasks. They make it a powerful tool for both research and industrial applications. Investing in the right add-ons allows for a tailored microscopy setup that meets your needs.
The Future of Condenser Microscopy
As technology advances, condenser microscopes continue to evolve. Scientists and engineers work hard to enhance their precision and functionality. The result is a steady stream of innovations improving microscopy.
Technological advancements
Recent advancements in condenser microscope tech are exciting. New features like digital integration are common. This means microscopes now connect to computers for easier data analysis. High-definition cameras are also standard. They capture clear images for further study. Automated stage controls are another advancement. They allow for precise sample movements during observations. These improvements make research quicker and more accurate.
Enhanced lighting systems are now in place. LED lights provide brighter, more consistent illumination. They also last longer than traditional bulbs. Modern condensers come with better lenses too. These reduce distortions and improve image quality.
In software, we see smart programs that assist in image processing. They can even analyze samples automatically. This takes some work off the researchers’ shoulders. The goal is to make every aspect of microscopy more efficient.
Trends and predictions in microscope development
Looking forward, we expect more digital and automated features. AI and machine learning could play bigger roles. They may assist in identifying patterns and abnormalities in samples. This could revolutionize how we understand microscopic worlds.
New materials are likely to improve microscope components. These materials will make devices lighter and more durable. There’s also a trend toward portability. Compact microscopes could soon be just as powerful as their larger counterparts.
Sustainability is another focus. Future designs may use less energy and environmentally friendly materials. This will lessen labs’ carbon footprints. The drive towards affordability is also important. It aims to make these tools available to more institutions worldwide.
In summary, condenser microscopy is set for exciting enhancements. These will expand its uses and increase accessibility across the globe.