Introduction to Microscopy
Microscopy allows us to see the unseen. It’s a tool that magnifies minute details of tiny objects. How to use a microscope begins with understanding what it is. A microscope is an instrument that enlarges small objects. This lets us study materials at a cellular or even molecular level.
Why is this important? Microscopy opens a world of discovery. It transforms dots, strands, and blobs into cells, fibers, and structures. Knowing how to use a microscope properly can reveal hidden details in the natural world.
But microscopes are not just for scientists. Hobbyists, students, and curious minds also find them intriguing. They enable us to explore cells, insects, plants, and minerals up close. The journey of learning how to use a microscope also teaches us patience and precision.
Before diving deeper, let’s agree on a few key points. Safety comes first. Microscopes are delicate and require careful handling. Next, knowledge is crucial. Understand the parts of a microscope and their functions. Finally, practice is essential. The more you work with a microscope, the better your skills.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore different types of microscopes. Then, we’ll break down the main components you need to know about. And finally, we’ll go through a step-by-step guide on how to use a microscope effectively. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge to start your microscopic explorations.
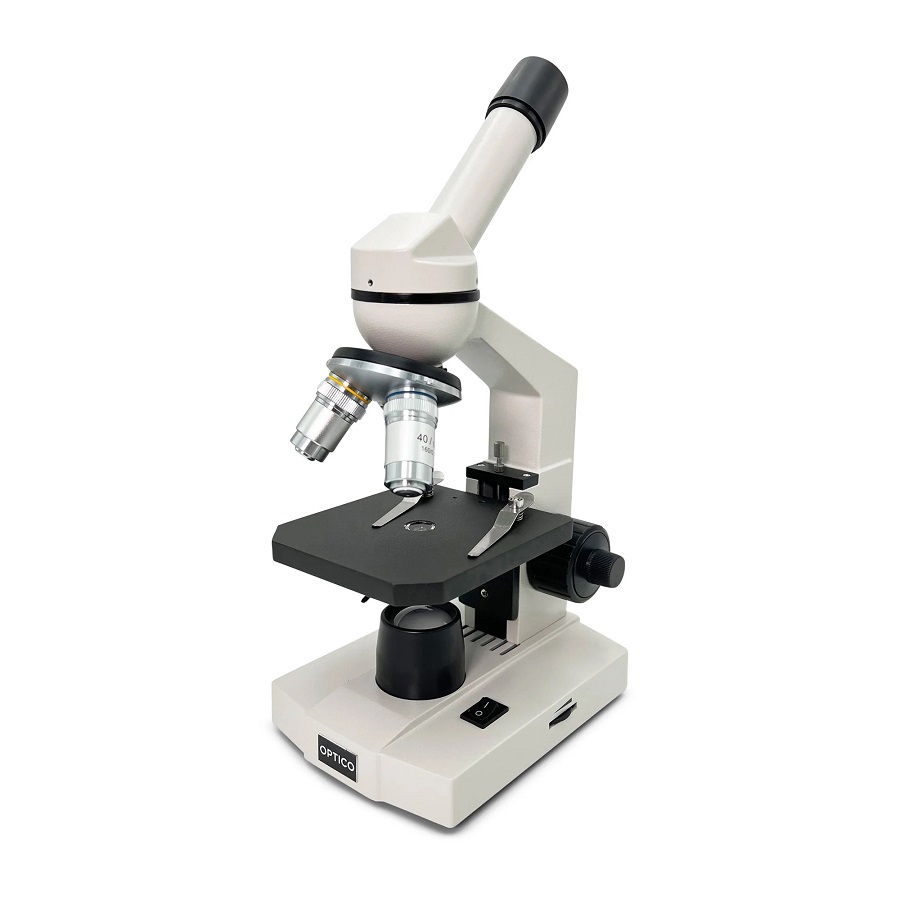
Types of Microscopes
Learning how to use a microscope encompasses understanding its various types. Each microscope serves a unique purpose and uses different methods to magnify objects.
Compound Microscopes
Compound microscopes are the classic tools most people picture. They have multiple lenses to achieve high magnification. The eyepiece and objective lenses stack to enhance small objects. Scientists often use these to examine cells, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
Stereo Microscopes
Unlike compound microscopes, stereo microscopes provide a 3D view of the specimen. Also known as dissecting microscopes, they’re great for larger objects. Users can observe insects, plants, or any material that requires less magnification and more depth.
Digital Microscopes
Digital microscopes are a modern twist in the microscopy world. They connect to computers or displays and show the magnified image on the screen. This makes sharing and analyzing images easier. They’re perfect for interactive learning and detailed analysis. It’s easy to store and share the digital data they produce.
Essential Microscope Components
To master how to use a microscope, it’s vital to know its essential components. Each part plays a specific role in magnification and viewing specimens. Below, we break down the parts that you’ll need to become familiar with.
The Eyepiece
The eyepiece is the part you look through. It usually contains a lens with 10x magnification. When you peer through the eyepiece, you see the amplified image of your specimen.
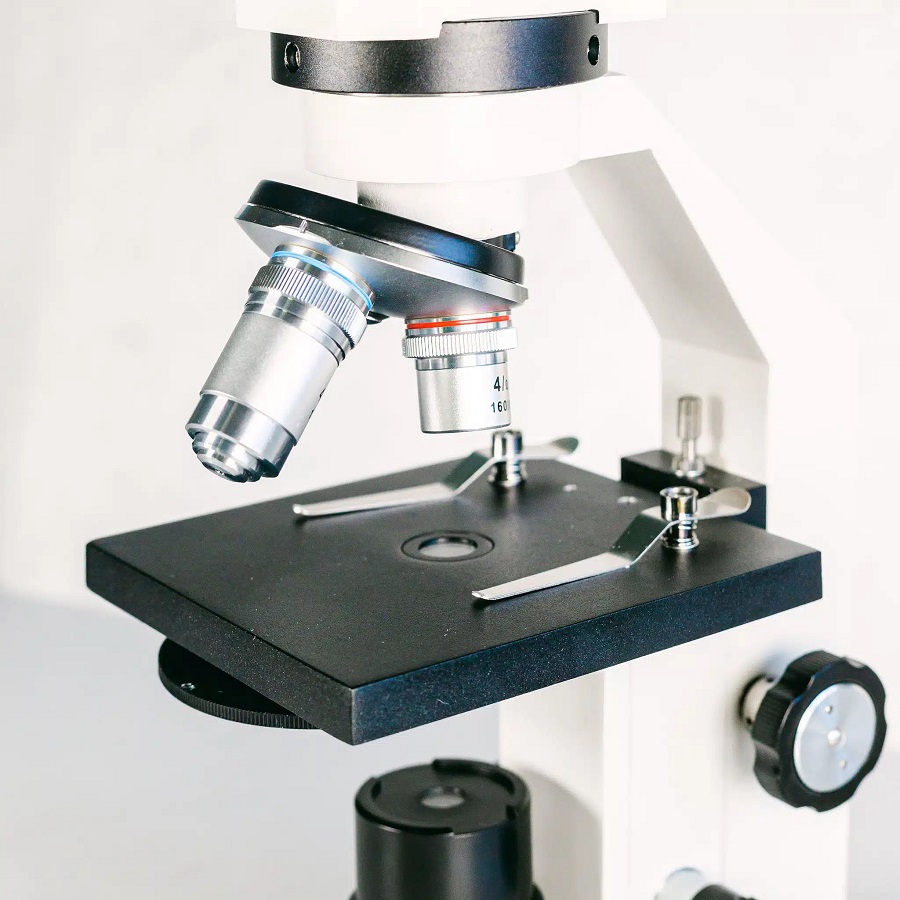
Objective Lenses
Objective lenses sit close to the specimen. These lenses come in different strengths, like 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. By rotating the lens turret, you switch between these lenses to change magnification levels.
Stage and Clips
The stage is the platform where you place your slides. Clips on the stage hold the slide in place. Proper placement ensures the specimen aligns with the objective lens for clear viewing.
Light Source
Microscopes have a light source below the stage. It shines light through the slide, making the specimen visible. Without proper lighting, details can be hard to see, even at high magnification.
Focus Knobs
Focus knobs adjust the lens’ distance to the specimen. Two types, coarse and fine, help you get a sharp image. The coarse knob brings the object into general focus, and the fine knob refines it.
By understanding these components, and with practice, you’ll enhance your skill in how to use a microscope effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Microscope
Grasping how to use a microscope is crucial for observing tiny wonders. This step-by-step guide will help you start your microscopic journey.
Preparing the Slide
Before using your microscope, prepare the slide properly. Clean the slide and cover slip. Place your specimen on the slide. Add a drop of water if needed. Carefully place the cover slip on top. Avoid air bubbles, as they can distort the image.
Setting Up the Microscope
Once the slide is ready, set up your microscope. Place the microscope on a stable surface. Ensure it’s near a power source if needed. Turn on the light source. Make sure the lowest power objective lens is in place. Secure the slide on the stage with the clips. Position it so the specimen is over the light source.
Focusing on the Specimen
Now, look through the eyepiece. Use the coarse focus knob to bring the specimen into view. It should look somewhat clear. Next, fine-tune the focus with the fine adjustment knob. The goal is to get a sharp image of the specimen.
Adjusting Magnification
If you need to see greater detail, adjust the magnification. Rotate the turret to switch to a higher power objective lens. Refocus the image each time you change the magnification. Be careful to prevent the lens from touching the slide, as this could damage both.

Tips for Maintaining Your Microscope
Maintaining your microscope is critical for its longevity and performance. Here are essential tips on how to keep your microscope in top condition:
Handle with Care
Always hold the microscope by its base and arm. Avoid touching the lenses with your fingers. This prevents damage and keeps the lenses clean.
Clean Regularly
Use a soft, lint-free cloth to wipe the exterior. For lenses, use lens paper and special cleaning solution. Gently remove any dust or oil without scratching the surfaces.
Avoid Moisture
Keep your microscope away from high humidity areas. Moisture can lead to mold growth and mechanical problems. Store it in a dry, cool place when not in use.
Cover When Not in Use
Use a dust cover to protect your microscope from airborne particles. This simple step can prevent a build-up of dirt that can affect image quality.
Routine Checks
Regularly check all moving parts. Make sure the focus knobs turn smoothly, and the stage clips are tight. Address any resistance or loose parts immediately.
Professional Servicing
Have your microscope serviced by a professional every few years. They can recognize and fix issues that may not be obvious to you. This keeps your microscope functioning well.
By following these tips, you’ll ensure that your microscope remains a reliable tool in your exploration of the microscopic world. Remember, good practices in handling and upkeep are part of learning how to use a microscope effectively.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When learning how to use a microscope, beginners can easily slip up. But don’t fret. By knowing these common pitfalls, you can steer clear and enhance your microscopy skills. Here’s what you should avoid:
Handling the Microscope Improperly
Handle your microscope with utmost care. Always grasp it by the base and arm. Don’t grab it by its eyepiece or lenses. This prevents accidental drops and protects the delicate parts.
Overlooking the Cleanliness of Components
Regular cleaning is a must. Do not overlook lint or smudges on the lenses. Use special lens paper, not regular tissue, to avoid scratches and maintain clarity.
Forgetting to Lock the Slide
Ensure your slide is securely clipped on the stage. A slide that moves during observation can disrupt your focus and be frustrating.
Using Incorrect Lighting
Too little or too much light can ruin the view. Don’t neglect to adjust the light source for optimal illumination of your specimen.
Being Overzealous with Focus Knobs
Turning focus knobs too harshly can damage the microscope or slide. Use gentle, gradual motions when focusing, particularly with the fine adjustment knob.
Ignoring the Limits of Magnification
Don’t jump to the highest magnification at once. Start with the lowest objective lens and work your way up slowly, refocusing as you go.
Neglecting Proper Storage
When not in use, cover your microscope. Store it in a dry, cool location. This prevents dust buildup and moisture damage.
By avoiding these mistakes, you position yourself for a rewarding microscopy experience. And remember, with each use, refine your technique to master how to use a microscope.
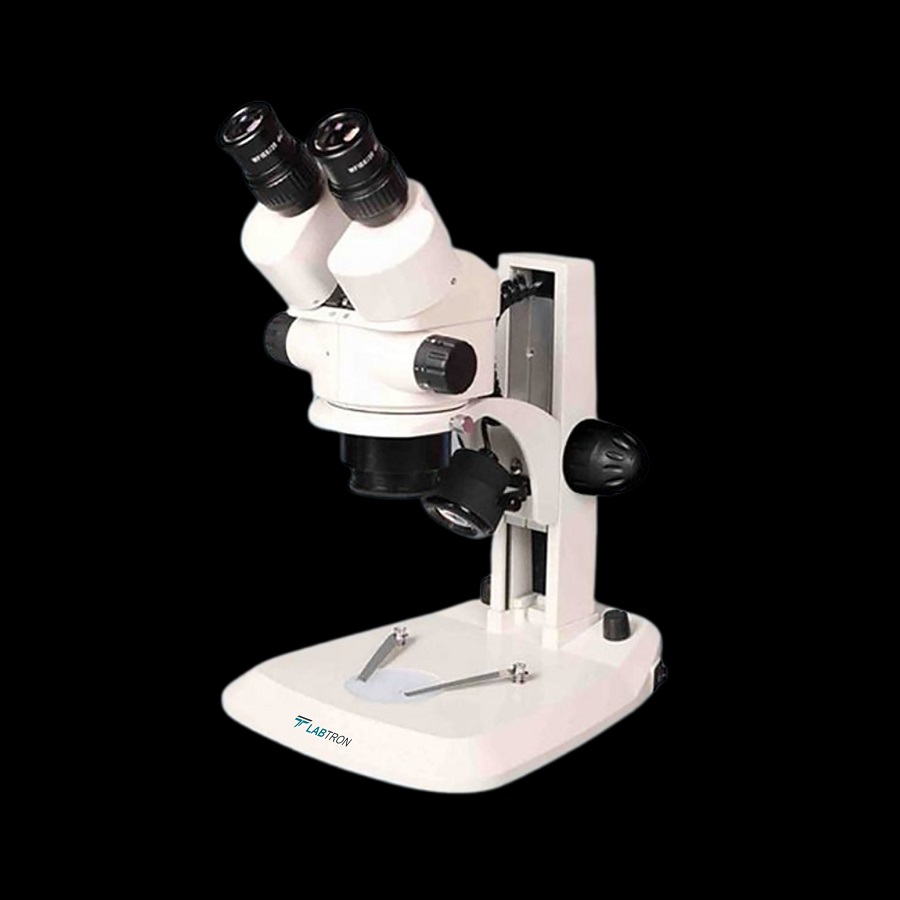
Applications of Microscopes in Different Fields
Microscopes are not just tools for scientists; they’re portals to tiny universes. Different fields use microscopes to unlock the secrets of the small scale.
Biological Sciences
In biological sciences, microscopes are indispensable. They help us see cells, tissues, and microorganisms. Medical researchers use them to understand diseases. Conservationists study plant and animal tissues. By using microscopes, biologists can see the building blocks of life.
Materials Science
Microscopes are key in materials science as well. They reveal the structure of metals, plastics, and ceramics. Engineers use them to make stronger materials. They test how materials act under stress. This leads to safer, more durable products.
Education
Education uses microscopes to spark curiosity. Students in schools and universities study the microscopic world. They learn how to use a microscope and about life’s complexity. Microscopes turn abstract concepts into real, visible examples. This hands-on learning builds a deeper understanding of science.
Recommended Resources for Further Learning
Once you grasp the basics of how to use a microscope, expanding your knowledge is key. Here are some top resources that can help you dive deeper into the world of microscopy.
Books and Manuals
Start with comprehensive books that cover different aspects of microscopy. Look for manuals that offer detailed illustrations and step-by-step instructions. Popular titles include ‘The Microscope and How to Use It’ and ‘Microscopes: A Tool of Science’.
Online Tutorials and Videos
Visual learners can benefit from online tutorials and videos. Search for microscopy lessons that are aimed at beginners. Websites like YouTube have a wealth of educational content created by experts or enthusiastic hobbyists.
Community Forums
Join forums where microscopy enthusiasts gather. Sites like MicroscopeForum.com allow you to ask questions, get advice, and share findings with peers.
Courses
Enroll in courses offered by educational institutions or online platforms. These often give you hands-on experience as well as a theoretical understanding. Basic biology or science courses also teach how to use a microscope as part of their curriculum.
Microscopy Clubs
If possible, find a local microscopy club. Engaging with a community of microscopists can provide invaluable practical tips and motivation.
Keep in mind that the best resource is practice. The more you use your microscope, the more proficient you will become. With these resources, continue your journey in the fascinating microscopic universe.
