Getting to Know Paramecium
What is Paramecium?
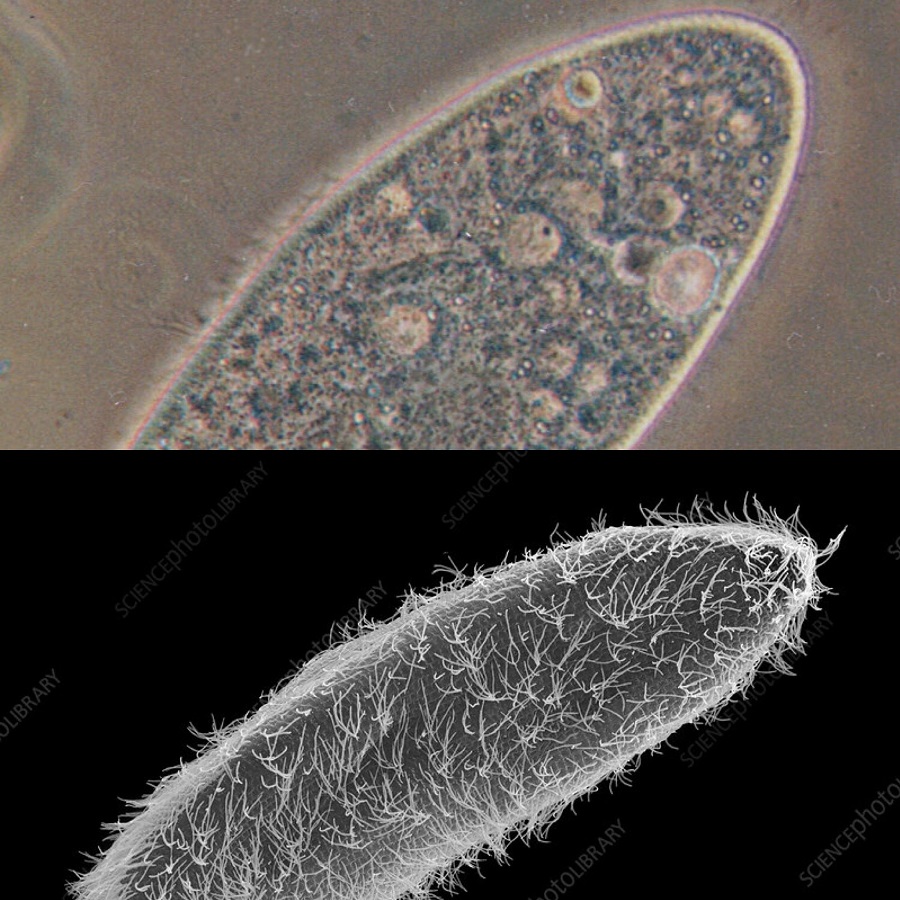
A paramecium is a single-celled organism with a slipper-like shape. It belongs to the kingdom Protista and thrives in freshwater habitats. Under a microscope, this microscopic marvel reveals intricate details. It moves using tiny hair-like structures called cilia. These cilia also help the paramecium feed on bacteria and other small particles.
Scientists often study paramecium due to its complex processes despite its simple structure. It has a core of genetic material and organelles that perform vital functions. Exploring a paramecium under a microscope can ignite curiosity and wonder about the micro-world.
The Habitat and Life Cycle of Paramecium
Paramecium finds home in still or slow-moving freshwater bodies. Ponds, lakes, and even puddles can host these organisms. They prefer environments rich in organic matter where they can feed and multiply.
The life cycle of a paramecium includes both asexual and sexual reproduction. It often reproduces by splitting into two. This is called binary fission. At times, they engage in a form of sexual reproduction known as conjugation. This process involves the exchange of genetic material with another paramecium.
Understanding the life cycle is central to grasping paramecium’s role in the ecosystem. It also sheds light on evolutionary processes among protozoa. With paramecium under microscope examination, one can witness these stages in fascinating detail.
Examining the Structure of Paramecium
Anatomy of a Paramecium
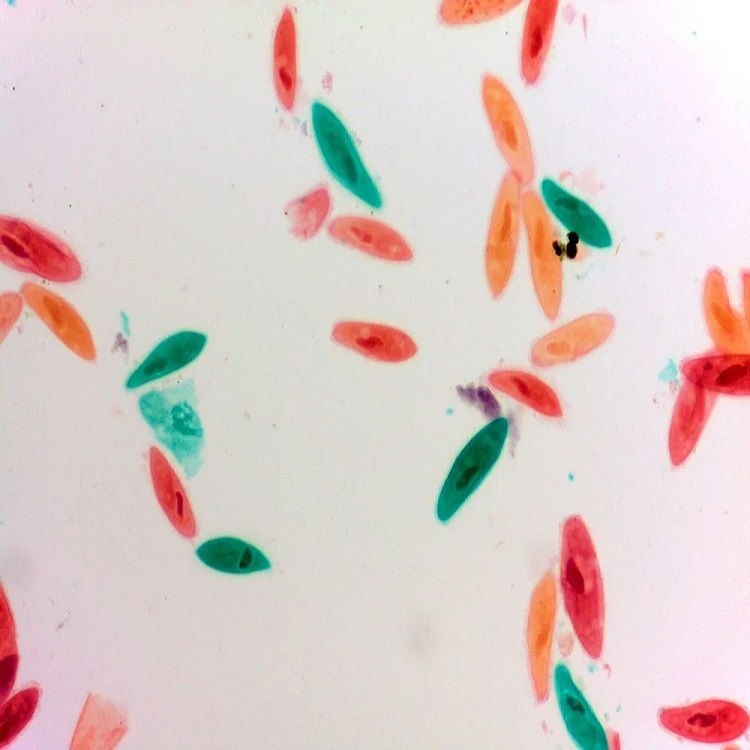
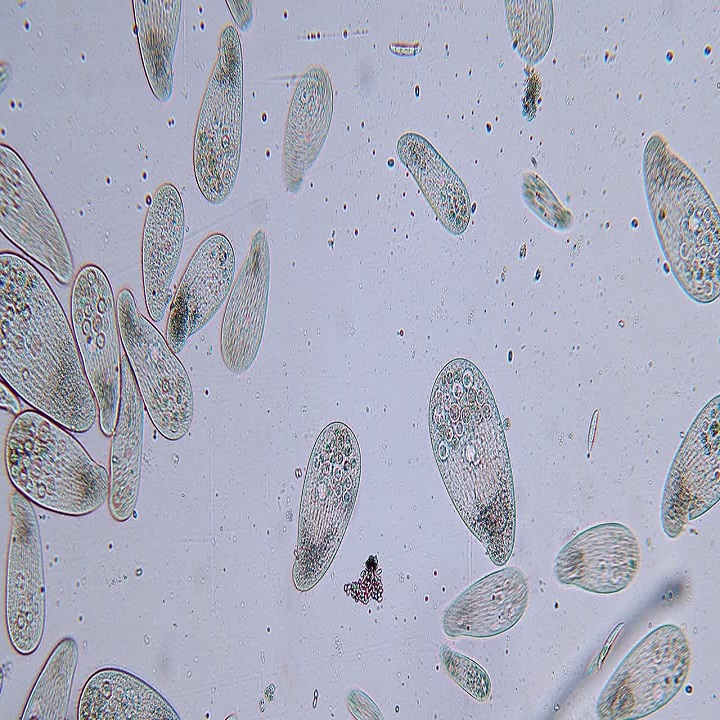
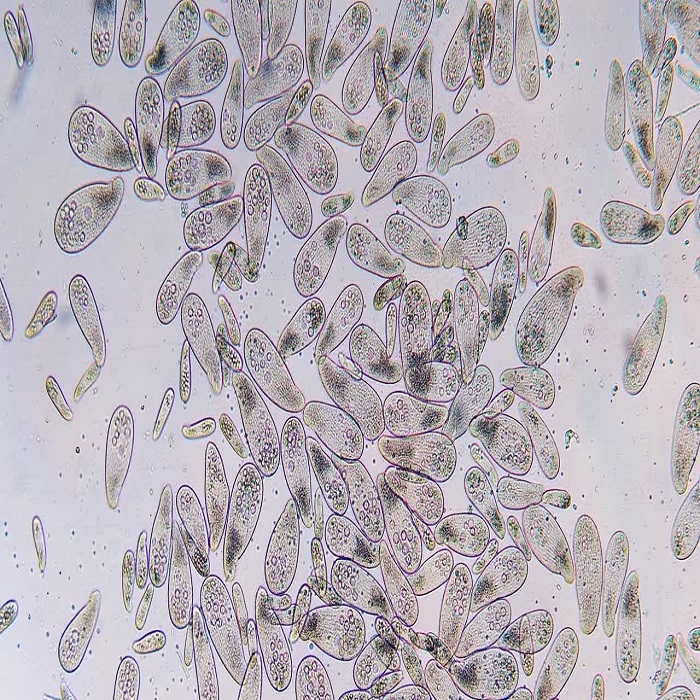
Observing a paramecium under microscope offers a glimpse into its complex anatomy. In shape, it resembles a tiny slipper, stretching roughly 0.05 to 0.32 millimeters in length. Its outer layer, the pellicle, maintains its shape while allowing flexibility. Inside, a paramecium boasts an array of organelles. It has a large, crescent-shaped macronucleus that controls non-reproductive functions. Beside it lies the smaller micronucleus, which plays a role in reproduction. Within the cytoplasm, you’ll find food vacuoles for digestion and contractile vacuoles that regulate water balance. These components collectively keep the paramecium alive and well.
Unique Features of Paramecium
The paramecium is not only known for its basic anatomical features. Its unique aspects capture the fascination of many. The cilia covering the paramecium give it mobility. They beat in coordinated waves, propelling the organism through its aquatic home. Another feature is the oral groove. This structure acts like a mouth, leading food particles towards the cell’s interior where digestion occurs. Moreover, paramecium can eject trichocysts as a defense mechanism. These are spear-like filaments that deter predators. Finally, let’s not forget the cytoproct. This serves as an exit for waste, illustrating the paramecium’s efficiency in processing nutrients and maintaining cellular health. Together, these features make studying paramecium under microscope a rich educational experience.
The Role of Paramecium in the Ecosystem
Paramecium as a Biological Indicator
Paramecium, observed under a microscope, fulfills a crucial role beyond its immediate survival. Its presence, or absence, indicates the health of freshwater ecosystems. Scientists often refer to such organisms as biological indicators. If paramecium thrives, it suggests a balanced environment with adequate resources. Conversely, a decline in these microorganisms could signal pollution or ecological disruption. Regular monitoring of paramecium populations can aid in environmental assessments. This makes the study of paramecium under microscope more than just academic.
Predator-Prey Relationships Involving Paramecium
Within their aquatic realms, paramecium sits in an intricate web of life. They serve as prey for larger microorganisms and small aquatic animals. Paramecium’s role as a primary consumer helps maintain the balance in food chains. By consuming bacteria and other tiny organisms, they process nutrients and make them available to their predators. This dynamic system of predator and prey plays out on a minuscule scale, with paramecium under microscope serving as a window into these vital ecological interactions.
Observing Paramecium: Preparation and Techniques
Setting up Your Microscope
To explore the world of paramecium under microscope, you need the right setup. First, ensure your microscope is clean. Wipe the lens with a special lens paper. Adjust the microscope’s light to a low setting. Place a drop of pond water on a slide. Carefully cover it with a cover slip. Now, your microscope is ready for paramecium observation. Do not forget to adjust the microscope stage. This helps in aligning the specimen correctly. Begin with a low magnification. Once you spot the paramecium, switch to a higher magnification for a closer look.
Tips for Observing Paramecium Under the Microscope
Here are some tips to get a clear view of paramecium under microscope. First, start with the lowest magnification. It makes finding paramecium easier. Once found, slowly increase magnification. This brings the details into sharper focus. Use the fine focus knob to clear up the image. If your microscope has it, use the diaphragm. This controls light and improves contrast. Be patient. Paramecium moves quickly. Staying patient helps in tracking and studying their behavior. Note their shape, cilia movement, and feeding habits. These observations provide a deeper understanding of paramecium’s life.
Scientific Discoveries Through Paramecium Study
The study of paramecium under microscope is not just fascinating, it has led to numerous scientific breakthroughs.
Historical Breakthroughs
Paramecium has been at the heart of many historical discoveries. In the 18th century, it helped to cement the idea of cilia as a means of locomotion. Researchers marveled at how these minute structures, observed in paramecium, could propel organisms through water. Studies of paramecium also advanced cell biology. They revealed how single-celled organisms handle complex tasks like digestion and reproduction.
Moreover, the understanding of genetic inheritance was refined through paramecium. Their mating process illustrated how traits are exchanged and passed down. These contributions from observing paramecium under microscope marked pivotal points in science history.
Recent Advances in Paramecium Research
In recent years, paramecium research has continued to evolve. Scientists use advanced imaging techniques to observe paramecium with unprecedented clarity. They discovered how its cilia work together in elaborate patterns to navigate. Some even unlocked secrets of paramecium’s immune response. They found how these cells fend off viruses, shedding light on potential medical applications.
Research on paramecium is also deepening our understanding of aging. By studying how paramecium age, scientists gain insights into the cellular processes that drive aging in more complex life forms. This ongoing study of paramecium under microscope keeps unveiling new layers of knowledge in cellular biology and beyond.
Photographic Journey: Capturing Paramecium Images
Techniques for Microscopic Photography
Documenting paramecium under microscope takes skill and careful technique. To start, attach a camera to your microscope. Choose cameras designed for microscopic imaging. They ensure high-quality photos. Adjust the microscope’s light to prevent glare. Glare can obscure paramecium details. Next, stabilize the camera. Movement can blur your images. Use a remote trigger to snap photos. This reduces camera shake. Also, select the right magnification. Too high magnification may make focusing difficult. Too low won’t capture fine details. Experiment with different settings to get the best results. Remember, patience is key. Wait for clear shots as paramecium moves.
Gallery of Paramecium
A gallery of paramecium images reveals the beauty of these organisms. Viewers can marvel at the intricate structures. See the whip-like cilia in action. Glimpse the oral groove collecting food. These photos showcase life unseen by the naked eye. They make understanding paramecium’s role in nature easier. A well-captured image can highlight the complexity of this single-celled organism spectacularly. Photographs of paramecium contribute to science and education. They let us appreciate the wonder of microscopic life.
The Educational Importance of Paramecium
Incorporating Paramecium into Science Curricula
Studying paramecium under microscope offers a practical learning experience for students. It introduces them to protists and cellular biology. Through observing paramecium, students grasp concepts like cell structure and cilia function. Teachers can use these organisms to demonstrate life processes like feeding and reproduction. Paramecium also simplifies learning about ecosystems. It shows how organisms fit into food webs and the impact of environmental changes. Including paramecium in lessons can spark interest in science among learners of all ages. It encourages critical thinking and curiosity. Overall, paramecium serves as an excellent tool for teaching key scientific principles.
Informal Learning: Paramecium in Home Education
Paramecium study fits well in home education. It supports hands-on learning and scientific inquiry. Families can explore biology with a simple microscope and pond water samples. This activity promotes observation skills and scientific reasoning. Home educators can create projects around paramecium. These can range from drawing to more in-depth research. Observing paramecium can also be a fun, affordable way to teach about the micro-world. It helps children appreciate the complexity of the simplest life forms. With its deep educational value, paramecium becomes a tiny teacher in our own homes.