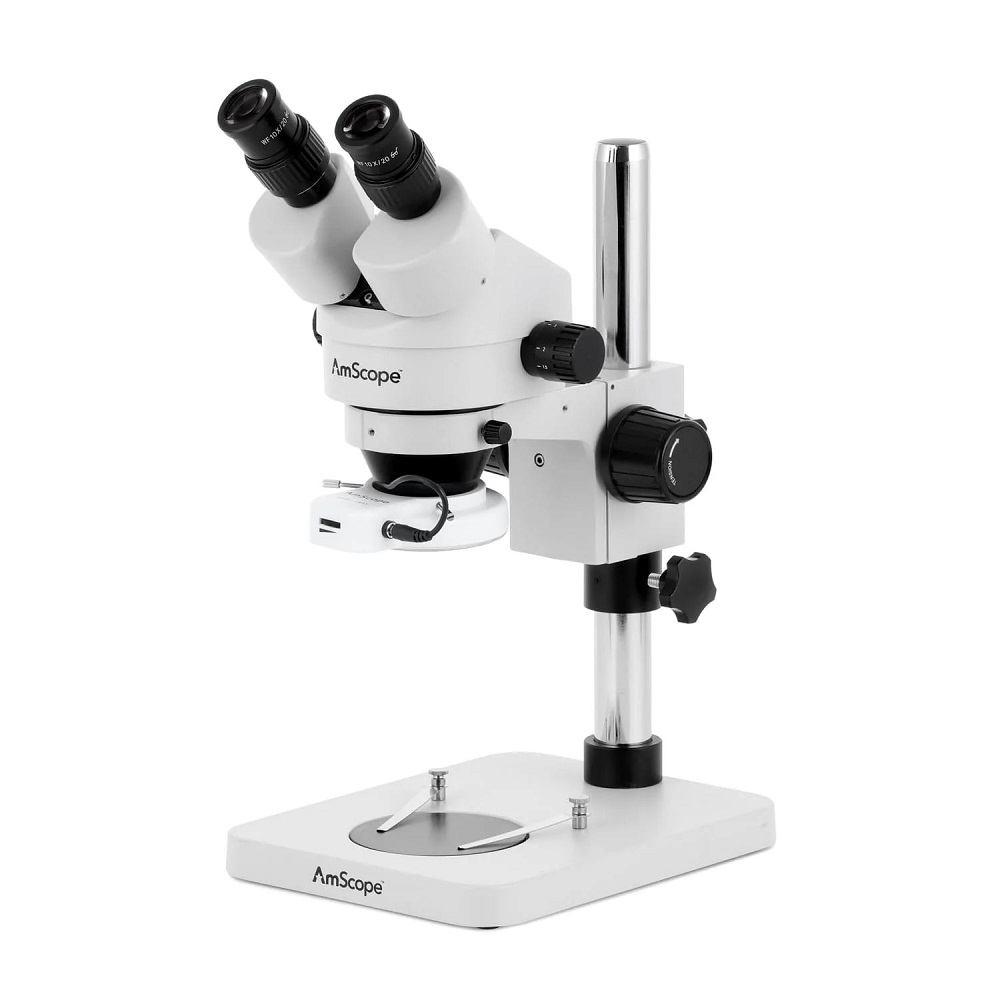
What Is a Dissecting Microscope?
A dissecting microscope, also known as a stereo or stereoscopic microscope, is a versatile tool. It allows users to view objects in three dimensions at low magnification. Unlike compound microscopes, which provide a more detailed view of tiny specimens, a dissecting microscope gives a broader view. This makes it perfect for observing larger, solid specimens like insects, plants, and electrical components.
What sets a dissecting microscope apart is its dual optical paths. It has two separate eyepieces that provide a slightly different angle of the same specimen. This results in a 3D image, enhancing depth perception. With this kind of microscope, users can work with their hands while looking into the eyepieces. This feature is essential for tasks like dissection, hence the name.
Dissecting microscopes generally have a higher working distance than other microscopes. This means there is more space between the lens and the object being viewed. The increased space allows for the manipulation of the specimen during observation or dissection. Additionally, many of these microscopes come with additional features. These may include a built-in light source to help illuminate the object, which is crucial for clear, detailed viewing.
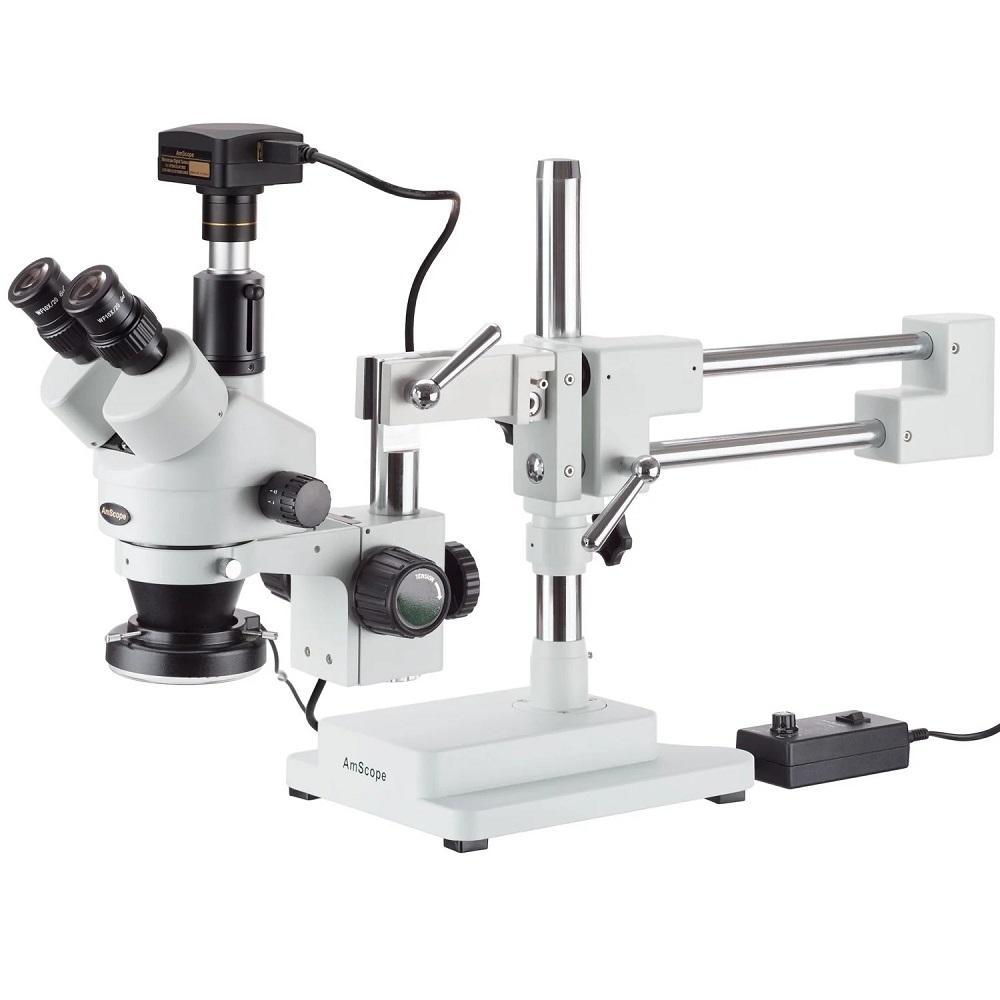

Key Features of Dissecting Microscopes
When selecting a dissecting microscope, it’s vital to understand its key characteristics. These features combine to make the microscope ideal for detailed observation and manipulation of specimens. Below are some essential attributes of dissecting microscopes.
- Stereo Viewing: Thanks to the separate optical paths for each eye, dissecting microscopes offer a stereo view. This enhances depth perception and provides a 3D visual experience.
- Magnification: While typically offering lower magnification than compound microscopes, dissecting microscopes still offer sufficient magnification. This range is perfect for larger specimens that don’t require extreme zoom.
- Working Distance: The space between the lens and the specimen is more generous in dissecting microscopes. This allows for better manipulation of the specimen under study.
- Illumination Options: Dissecting microscopes often come with built-in lights. These may include top or bottom illumination or even both, enabling clear views of the specimen.
- Adjustable Focus: Users can easily adjust the focus to examine different parts or layers of the specimen. Fine and coarse adjustments offer versatility and precision.
- Large Stage: The stage on these microscopes is usually bigger. It accommodates larger specimens and provides room for tools used during dissection.
- User-friendly Design: Designed for hands-on work, these microscopes often feature user-friendly controls. They are accessible and can be adjusted without shifting focus from the specimen.
Incorporating these key features, a dissecting microscope is an indispensable tool in various settings. From scientific research to educational laboratories, its capabilities are highly valued.
Applications of Dissecting Microscopes in Various Fields
Dissecting microscopes are not just limited to biology labs. Their versatility extends into many areas. Here, we examine the diverse applications of dissecting microscopes across different fields.
- Education: In educational settings, dissecting microscopes are indispensable for teaching biology. They allow students to observe the anatomy of larger specimens like insects and plants.
- Electronics: Technicians use dissecting microscopes for inspecting circuit boards. The high working distance is ideal for soldering and repairs.
- Jewelry Making: Jewelers rely on dissecting microscopes to inspect and work on intricate pieces. The stereo view helps in assessing gem quality and detailing.
- Forensic Science: In forensics, these microscopes assist in examining evidence such as fibers and fingerprints.
- Botany: Botanists study plant structures with dissecting microscopes. They can view the organism’s 3D complexity without disturbing the specimen.
- Entomology: Entomologists, or insect scientists, use dissecting microscopes to analyze insect parts. This is crucial in understanding their anatomy and behavior.
- Quality Control: In manufacturing, dissecting microscopes help in quality control. They allow for the close examination of products for defects.
Each of these fields benefits from the key features of dissecting microscopes, such as the large stage, stereo viewing, and adjustable focus. The ability to observe and manipulate objects in a 3D space makes the dissecting microscope a valuable tool across numerous industries.
How to Choose the Right Dissecting Microscope for Your Needs
Choosing the right dissecting microscope involves considering several factors. Here are key points to guide you:
- Assess Your Application: Think about the main use of your microscope. If you’re in education, you may need a basic model. For intricate electronics work, you might want higher magnification.
- Magnification Needs: Consider how much magnification you require. Dissecting microscopes offer various ranges, so pick one that suits your specimens.
- Working Distance: Make sure the working distance fits the size of objects you’ll examine. A longer distance is useful for larger or manipulated samples.
- Illumination: Good lighting is essential. Decide if you need top, bottom, or dual illumination based on your specimens.
- Ergonomics: Comfort matters. Look for a design that won’t strain your posture during long periods of use.
- Quality of Optics: High-quality lenses produce clearer images. Invest in a microscope with superior optics for the best results.
- Budget: Set a budget that reflects your needs. Remember, the cheapest option may not always meet your long-term requirements.
- Durability and Warranty: Check for a sturdy build and inquire about warranty options. A good warranty can save costs on future repairs or replacements.
Taking time to evaluate these aspects will help ensure you find a dissecting microscope tailored to your specific needs. Remember to balance functionality with your budget to make a smart investment.
Operating a Dissecting Microscope: Basic Procedures
To successfully use a dissecting microscope, follow these simple steps:
- Prepare Your Specimen: Start by correctly preparing your specimen. Place it securely on the stage without obscuring your view.
- Adjust the Eyepieces: Set the eyepieces to match the distance between your eyes. This ensures a clear stereo image.
- Focus Your Image: Use the focusing knobs to bring your specimen into sharp view. Begin with coarse adjustment, and then use fine tuning.
- Optimize Illumination: Turn on and adjust the built-in lights for the best view. Decide whether top, bottom, or both lights are necessary for your specimen.
- Manipulate as Needed: If you’re dissecting, you can now manipulate the specimen. The high working distance allows for precise work with tools.
- Adjust Magnification: If needed, switch to different magnification levels. Remember, dissecting microscopes have lower magnification for larger objects.
- Use Both Eyes: Look through both eyepieces to maintain the 3D perspective and depth perception.
- Take Breaks: Avoid eye strain by taking regular breaks from the eyepieces, especially during long sessions.
Using a dissecting microscope is a hands-on skill that improves with practice. Always handle your specimen and the equipment with care to ensure accurate results and maintain the integrity of your dissecting microscope.
Comparing Dissecting Microscopes With Other Types
When considering a dissecting microscope, it is crucial to understand how it differs from other microscopes. This knowledge ensures that you choose a microscope suited to your specific requirements. Here are some contrasts between dissecting microscopes and other commonly used types.
- Magnification Levels: Dissecting microscopes typically have lower magnification capabilities compared to compound microscopes. This is perfect for viewing bigger, thicker specimens like insects, plants, and small mechanical parts.
- Depth Perception: Due to their stereo view, dissecting microscopes excel in providing three-dimensional visualization. This allows for depth perception which compound microscopes, with their single optical path, cannot offer.
- Working Distance: Another key advantage of dissecting microscopes is the extended working distance. This feature makes them ideal for tasks that require manipulating the specimen, unlike the close proximity needed in compound and electron microscopes.
- Field of View: Dissecting microscopes present a wider field of view. This allows the observer to see more of the specimen’s surroundings, unlike the narrow field of view in high-power compound microscopes.
- Ease of Use: With their user-friendly design, dissecting microscopes are simpler to handle for beginners. They do not require thin specimen slides, making them more straightforward compared to compound or electron microscopes that require extensive sample preparation.
- Versatility in Lighting: The built-in top and bottom illumination options in dissecting microscopes offer flexibility in viewing various specimen types. In contrast, most compound microscopes only have bottom illumination.
In summary, dissecting microscopes are the preferred choice for viewing larger, three-dimensional objects. They provide an easy-to-use platform for both educational and detailed professional work. While they offer lower magnification, they make up for it in their enhanced depth perception and working distance. This makes them distinct from other types of microscopes used in scientific and industrial fields.
Maintenance and Care for Dissecting Microscopes
Maintaining your dissecting microscope ensures long-term performance and accuracy. Proper care involves a few straightforward steps.
- Clean Regularly: Wipe lenses with a soft, lint-free cloth. Use lens cleaner if needed. Dust off the body and stage with a gentle brush.
- Handle with Care: Always lift the microscope by its base and arm. Avoid holding it by its eyepieces or lenses.
- Store Properly: When not in use, cover the microscope with a dust cover. Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment.
- Check Light Sources: Inspect and replace bulbs as necessary. Ensure lighting components are functioning correctly for optimal illumination.
- Avoid Moisture: Keep the microscope away from liquids. If a spill occurs, dry immediately and thoroughly.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check for loose screws or components. Tighten and adjust as needed to keep the microscope stable.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule professional maintenance annually. Experts can calibrate and make precise adjustments.
- Usage Training: Educate users on correct operation. This reduces wear and tear from improper handling.
By following these care guidelines, your dissecting microscope will remain a reliable tool in your professional or educational toolkit.
Advancements and Innovations in Dissecting Microscope Technology
Over the years, dissecting microscope technology has seen significant advancements. Innovations aim to enhance user experience and improve precision. Here’s how modern technology has enhanced dissecting microscopes.
- Digital Imaging: Newer models feature built-in digital cameras. They allow easy capture and sharing of images.
- LED Illumination: Modern dissecting microscopes often have LED lights. These provide bright, energy-efficient lighting and a cooler work environment.
- Zoom Capabilities: Advanced microscopes offer smoother zoom functions. Users can magnify specimens without losing focus or clarity.
- Ergonomic Design: Designs now focus on user comfort. Features like adjustable eyepiece angles and height help reduce strain during long use.
- Software Integration: Some dissecting microscopes can connect to software. This allows for image analysis and measurement directly on a connected computer.
- 3D Imaging: Cutting-edge technology offers enhanced depth perception. This gives a more detailed view of the specimen’s topology.
- Portability: Compact and lightweight models are now available. These make the microscopes easier to move and set up in different locations.
These advancements help users work more efficiently. They also expand the possibilities for research and education. It is an exciting time for the field of microscopy as we witness these continuous improvements.
