In the world of scientific research and laboratory work, precision and reliability are paramount. One of the essential tools that ensure accuracy in liquid handling is the pipettor. To maintain the optimal performance of your pipettor, understanding and managing pipettor parts is crucial. This guide delves into the various components of pipettors, their functions, maintenance tips, and how to choose the right parts to enhance your laboratory efficiency.
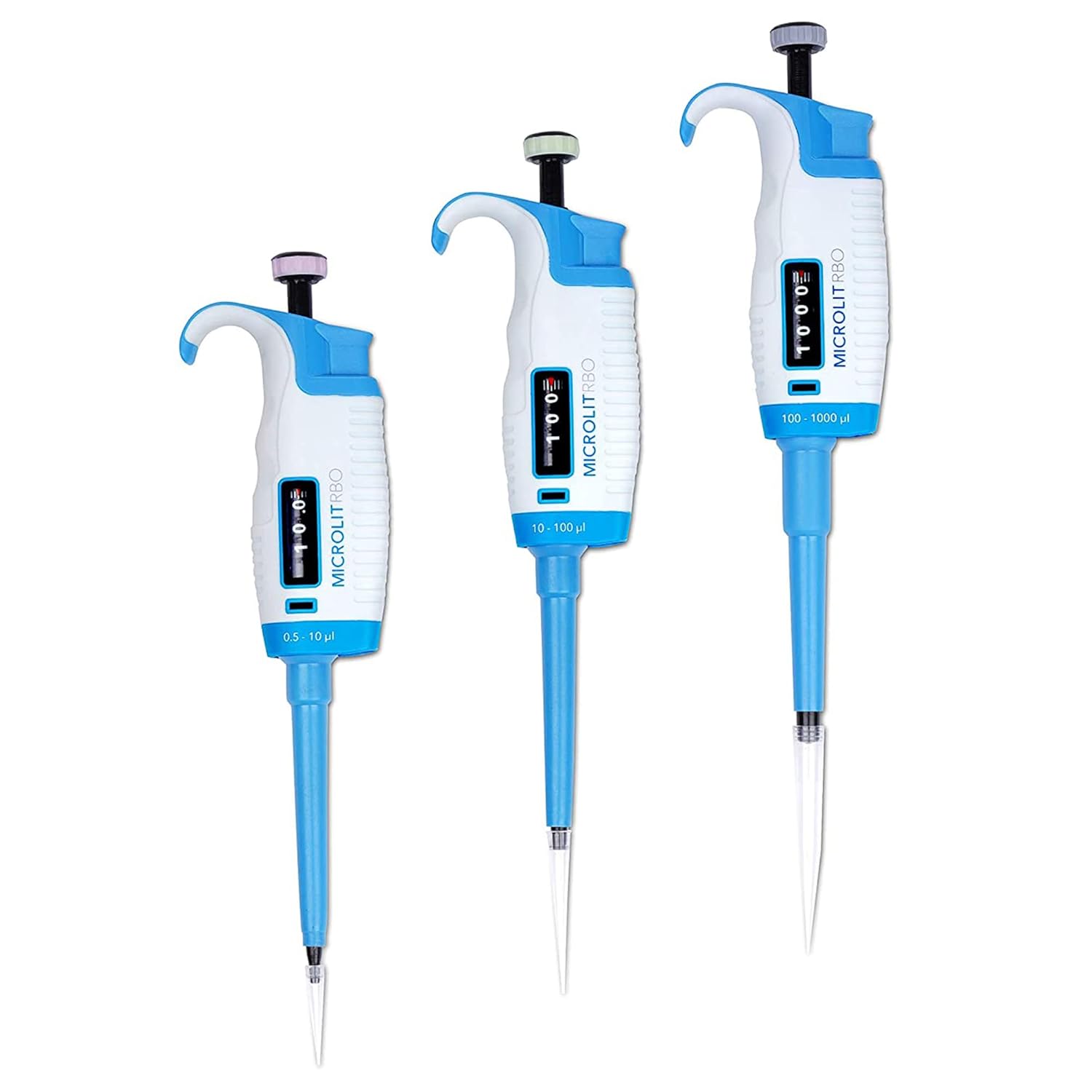 Introduction to Pipettors
Introduction to Pipettors
Pipettors are essential tools commonly used in laboratories. They allow precise transfer of liquids in small volumes. Understanding their parts and functions is crucial for accurate laboratory work.
What is a Pipettor?
A pipettor is a device designed to measure and transfer liquid volumes accurately. It is commonly used in biological, chemical, and clinical labs. The device consists of multiple interchangeable parts that function to draw and dispense liquids precisely. Pipettors are available in different designs, such as manual or electronic models.
Importance of Pipettors in Laboratories
Pipettors ensure accuracy and reproducibility in experiments and tests involving liquid handling. They help researchers avoid errors in liquid measurements, which can affect experimental results. Whether performing DNA analysis or chemical titrations, pipettors are vital for consistent and dependable lab processes.
Key Components of a Pipettor
Understanding the key components of a pipettor is essential for its effective use. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to the pipettor’s overall accuracy and reliability.
Handle and Plunger Assembly
The handle provides a comfortable grip for the user. The plunger is used to control liquid movement. Pressing the plunger draws liquid into the pipette tip. Releasing it dispenses the liquid. Together, these components ensure efficient liquid handling.
Volume Adjustment Mechanisms
Volume adjustment mechanisms let users set specific liquid volumes. A dial or knob usually controls this feature. Properly set volumes ensure accurate measurements. This is important for experimental consistency and reproducibility.
Tip Ejector System
The tip ejector system removes used pipette tips effortlessly. This feature prevents contamination risks. It usually functions with a simple button press. This system enhances workflow efficiency in busy labs.
Pipette Tip and Compatibility
The pipette tips are disposable parts that hold the liquid. They come in various sizes for different pipettors. Compatibility between tips and pipettors is crucial for precision. Incorrect tips can cause inaccurate measurements or leaks.
By understanding these components, you can operate pipettors more effectively and avoid common errors.
 Types of Pipettors and Their Parts
Types of Pipettors and Their Parts
Pipettors come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Understanding these types and their parts helps in choosing the right tool for precise liquid handling.
Single-Channel vs. Multi-Channel Pipettors
Single-channel pipettors handle one liquid sample at a time. They are ideal for tasks requiring individual liquid transfers, such as preparing solutions or loading individual wells in a microplate. These pipettors are often used in experiments where precise and manual control is needed.
Multi-channel pipettors, on the other hand, can handle multiple samples simultaneously. They are equipped with multiple channels, usually 8 or 12, making them perfect for high-throughput tasks like filling multi-well plates. This type saves time and ensures consistency across repetitive processes.
Manual vs. Electronic Pipettors
Manual pipettors rely entirely on the user for operation. The plunger and volume adjustments are manually controlled. They are cost-effective and often lighter, making them convenient for prolonged use. However, they require more user effort and precision.
Electronic pipettors offer automated operation, reducing user fatigue and increasing precision. They feature motorized plunger control, enabling consistent liquid movement. Electronic models are also programmable, providing advanced functions like variable speed and mixing. While they are often more expensive, electronic pipettors are indispensable for complex and repetitive tasks.
Choosing between these types depends on your laboratory’s needs. Factors like task volume, precision requirements, and user comfort play an important role in the selection process.
Functions of Each Pipettor Part
Understanding the function of each part improves the accuracy and reliability of pipettors.
How the Plunger Works in Liquid Aspiration and Dispensing
The plunger controls liquid movement in the pipettor. Pressing it aspirates liquid into the pipette tip. Releasing it dispenses liquid accurately. Proper plunger operation ensures consistent and precise measurements.
Role of the Tip in Precision and Accuracy
The pipette tip holds and transfers liquid. Disposable tips prevent contamination between experiments. Correct tip size improves measurement accuracy and reduces liquid loss. Tips must match the pipettor for optimal performance.
Importance of Seals and O-Rings in Preventing Leaks
Seals and O-rings ensure airtight connections in the pipettor. They prevent liquid leaks during operation. Worn seals can lead to inaccurate measurements and reduced efficiency. Regular inspection keeps these parts functional and reliable.
 Maintenance and Care for Pipettor Parts
Maintenance and Care for Pipettor Parts
Regular maintenance ensures pipettor accuracy and extends its lifespan. Proper care minimizes contamination and operational issues. Below are key practices for keeping your pipettor in top condition.
Cleaning and Sterilization Techniques
- Disassemble the Pipettor: Remove detachable parts like tips, seals, and O-rings.
- Clean Components Thoroughly: Wipe external surfaces with alcohol-based solutions. Use mild detergent for internal parts.
- Autoclave Where Necessary: Autoclave only parts designated as autoclavable by the manufacturer.
- Allow Components to Dry: Let all parts air-dry completely before reassembly.
Routine cleaning ensures precision and prevents cross-contamination. Always follow the manual for specific cleaning guidelines.
Tips for Preventing Wear and Tear
- Avoid Over-Tightening Components: Over-tightening reduces the lifespan of seals and O-rings.
- Use Compatible Pipette Tips: Mismatched tips can damage the pipettor and affect measurements.
- Store Properly: Keep pipettors in a vertical position or designated holder to avoid damage.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping the pipettor as impact can disrupt calibration.
Preventive care preserves the functionality of your pipettor parts and reduces costly repairs.
Common Troubleshooting for Malfunctioning Parts
- Inconsistent Measurements:
- Check if the pipette tips are tightly secured.
- Inspect seals and O-rings for wear or leaks.
- Difficulty Ejecting Tips:
- Clean the tip ejector system to remove residue buildup.
- Ensure the tip ejector is properly aligned.
- Stiff Plunger Movement:
- Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the user manual.
- Ensure no obstructions are interfering with the plunger.
- Leaking Liquid:
- Replace worn seals or damaged O-rings promptly.
- Confirm that pipette tips are compatible and securely attached.
By following these techniques, you can maintain pipettor parts, ensuring reliable and accurate performance.
Tips for Choosing the Right Pipettor and Parts
Selecting the ideal pipettor and parts is essential for precise and efficient liquid handling. Making the right choice depends on various factors, ranging from task requirements to compatibility.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pipettor
- Application Needs: Determine the type of experiments or applications you will perform. For high-throughput tasks, choose multi-channel pipettors. For specific and detailed work, use single-channel models.
- Volume Range: Consider the liquid volumes you handle frequently. Select a pipettor that offers appropriate volume adjustments.
- Usability: Ensure ease of use and comfort during operation. Lightweight manual pipettors are great for extended use. For repetitive tasks, electronic models reduce user fatigue.
- Durability: Choose models with robust designs to withstand repeated use. Reliable seals and O-rings ensure long-lasting performance.
- Budget: Balance cost with features. Manual pipettors are cost-effective, while electronic pipettors offer better automation at a higher expense.
By evaluating these aspects, you can select a pipettor tailored to your lab’s requirements.
Compatibility of Replacement Parts with Different Brands
- Pipette Tips: Ensure the pipette tips match your pipettor model. Incorrect tips can cause measurement errors.
- Seals and O-Rings: Replacement seals should fit accurately to maintain airtight connections. Compatibility prevents leaks.
- Volume Adjustment Knobs: If a knob is replaced, verify it functions seamlessly with the original design.
- Universal Fit Parts: Some brands offer universal parts compatible with other models. Check specifications carefully.
- Technical Support: Reach out to manufacturers to confirm if replacement parts work with your pipettor brand.
Using compatible parts keeps your pipettor functioning flawlessly. Regular checks prevent operational problems and ensure reliable performance.
 Innovations in Pipettor Design
Innovations in Pipettor Design
Cutting-edge innovations in pipettor design aim to improve efficiency, precision, and environmental sustainability. These advancements reflect the evolving needs of modern laboratories.
Recent Advancements in Pipettor Technology
- Automated Pipetting Systems: Advanced pipettors now feature automation, reducing manual effort and human error. These systems often include robotic arms to perform repetitive liquid handling tasks with high accuracy.
- Ergonomic Enhancements: New designs prioritize user comfort, reducing strain during prolonged use. Lightweight materials and ergonomic grips improve precision and ease.
- Enhanced Precision Mechanisms: Technology such as digital sensors ensures consistent volume settings for unmatched reproducibility. Some pipettors also feature real-time feedback on liquid dispensing accuracy.
- Programmable Pipettors: Electronic models now offer customizable programs for complex or repetitive tasks. These advanced features include multi-dispensing and stepwise dilution, streamlining processes in high-throughput labs.
- Wireless Connectivity: Integration with wireless technology allows data tracking and remote monitoring of pipetting tasks. This feature is particularly useful in automated workflows and quality control.
Environmental Considerations for Pipettor Parts
Sustainability is increasingly important in laboratory practices. Here’s how to manage pipettor parts with environmental considerations in mind:
Eco-Friendly Materials
Choose pipettor parts made from eco-friendly materials that reduce environmental impact. Sustainable materials contribute to responsible laboratory practices and promote environmental stewardship.
Recycling and Disposal
Properly dispose of worn or damaged pipettor parts to minimize environmental harm. Implement recycling programs for components that can be repurposed, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing
Support suppliers that prioritize energy-efficient manufacturing processes for pipettor parts. Energy-efficient production minimizes carbon footprints and aligns with sustainable laboratory practices.
Longevity and Reusability
Opt for high-quality, durable pipettor parts that offer longevity and reusability. Investing in long-lasting components reduces the frequency of replacements, leading to less waste and lower environmental impact.
Training and Education on Pipettor Parts
Proper training on the use and maintenance of pipettor parts is vital for laboratory efficiency and safety. Educate your team on the following aspects:
Understanding Component Functions
Ensure that laboratory personnel understand the functions of different pipettor parts. Knowledge of each component’s role helps in proper handling, maintenance, and troubleshooting of issues.
Proper Handling Techniques
Train staff on the correct handling techniques for pipettor parts to prevent damage and ensure longevity. Proper handling includes careful installation, cleaning, and storage practices.
Maintenance Procedures
Educate team members on the maintenance procedures for pipettors, including regular cleaning, lubrication, and calibration. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of pipettor parts and ensures consistent performance.
Troubleshooting and Repairs
Provide training on how to troubleshoot common pipettor issues and perform minor repairs. Empowering your team with troubleshooting skills reduces downtime and dependence on external support.
Safety Protocols
Emphasize the importance of safety protocols when working with pipettor parts. Safe practices prevent accidents and ensure a secure laboratory environment.
 Future Trends in Pipettor Parts Development
Future Trends in Pipettor Parts Development
The pipettor industry continues to advance, introducing innovations that enhance laboratory efficiency and precision. Here are some future trends in pipettor parts:
Automation and Robotics Integration
Future pipettor parts will increasingly integrate with automation and robotics systems, enhancing the precision and speed of liquid handling in high-throughput laboratories.
Advanced Sensor Technology
Incorporating advanced sensors into pipettor parts will provide real-time feedback on liquid handling, improving accuracy and reducing human error in laboratory processes.
Customizable Components
Developers are focusing on creating customizable pipettor parts that can be tailored to specific laboratory needs, offering greater flexibility and functionality in diverse research environments.
Enhanced Connectivity
Improved connectivity features in pipettor parts will allow for seamless integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS), facilitating better data tracking and analysis.
Smart Diagnostics
Smart diagnostics in pipettor parts will enable predictive maintenance, alerting users to potential issues before they cause significant disruptions. This proactive approach ensures continuous and reliable pipettor performance.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing pipettor parts is essential for maintaining the precision and reliability of your pipettors in the laboratory. By familiarizing yourself with the key components, performing regular maintenance, and choosing high-quality parts from reputable suppliers, you can ensure that your liquid handling processes remain accurate and efficient. Additionally, staying updated with the latest innovations and implementing best practices for inventory management and sustainability will further enhance your laboratory’s productivity and environmental responsibility. Invest in the right pipettor parts today to safeguard the integrity of your research and enjoy peace of mind in your scientific endeavors.